Spectrum Rotate
Contents
Introduction
This tool is used to obtain the Fourier amplitude spectra in the horizontal plane, i.e., as a function of azimuth, from any type of 2D vibration signals (ambient vibrations, earthquake…). The example used for explanations is an ambient vibration recording on soil.
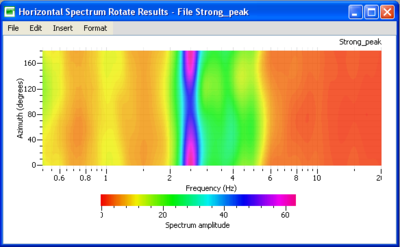
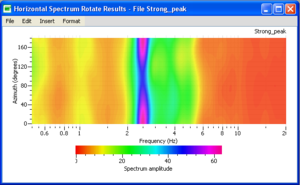
Here, a series of spectra is calculated from 0° to 180° every 10 °, and is presented in a frequency-azimuth graphic. This graphic can be used to analyse the repartition of the energy in the horizontal plane. Results are displayed between 0° and 180°, the 180-360° being a symetry of the 0-180°.
As for the other tools, the data can be processed:
- from a graphic viewer, to verify the windowing and to display the results;
- from a table. In this case, Geopsy will display only the resulting curves.
A global description of the Spectrum rotate Toolbox is available for more details.
This tool is very similar to the Spectrum Toolbox in its use.
There are only two differences between this tool and the Spectrum tool:
- there is no possibility to save a file with the spectrum curve. Of course, it is always possible to save the graphics;
- the computing of the Fourier amplitude spectra implies synchronous windows.
Getting ready
- Download compressed signal file. If the file has been already downloaded (as for H/V or Spectrum purposes for example), do not download it again.
- Load and view these downloaded signals.
- Select Spectrum Rotate in menu Tools (alternative ways to start a tool)
Window selection
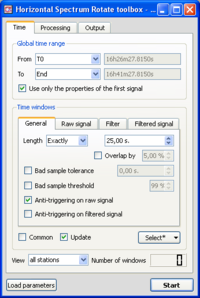
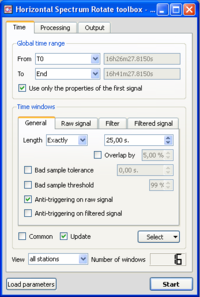
This part is devoted to define how the windowing will be calculated:
-use of an anti-trigger (LTA/STA) or not ?
-are bad sample accepted (and how many) ?
-overlap of the windows or not ?
-...
- Make sure you are in the Time Tab, and that parameters are as in the example window. The Anti-triggering on raw signal button has been checked.
- To make sure that parameters are set up alright, it is possible to download the compressed parameter file and load toolbox parameters.
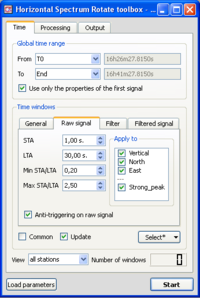
- Click on the Raw signal, to check that anti-trigger parameters are as in the example window.
- Click on the Select button and select Auto into the pop-up menu.
- The number of selected windows appears at the bottom right corner of the time tab. The number of windows should be as in the example.
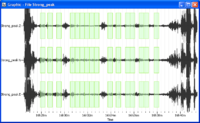
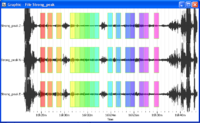
- Selected windows should appear as green rectangles on the signal viewer. Here, the windows are synchronous on the three components as we required a common windowing.
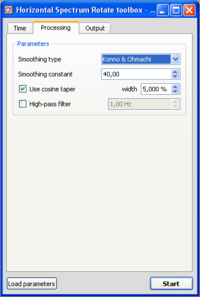
Processing parameters
- Click on the Processing tab, and make sure that parameters are as in the example window.
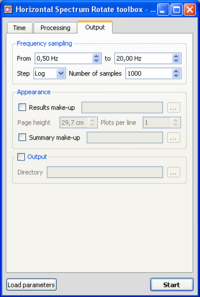
Output parameters
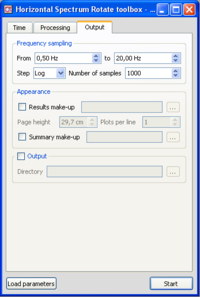
- Make sure you are in the Output tab, and that parameters are as in the example window.
- As mentioned before, it is impossible to save the curves in ASCII format.
Data processing
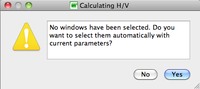
- In case no window selection has been performed, a pup-up window appears.
Simply click on the Yes button and processing will follow its way.
Results
Signal display
- Selected windows are colored.
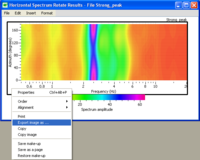
Spectrum Rotate Graphic
- The 0° direction indicates the North direction
- The 90° direction indicates the East direction
- Below the graphic displaying the the spectral content, there is a palette that allows the user to change the colouring characteristics of the graph.
Changing spectrum graphics appearance
- It is possible to change the appearance of the spectrum graphics at the user's will using a make-up.
Saving results
There are two solutions to save the results graphically. The first one allows saving each individual graph in independant files and the second allows saving all the graphics onto the graphic window in a single file.
- Saving the graphs in individual files
- The spectrum graphics may be saved in various image formats.
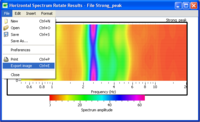
- Right click in the left hand margin of the spectrum graphic.
- In the pop-up menu, choose Export image. Then choose a destination.
- Saving individual file does not allow to save the palette in the saved graphic.
- Saving all the graphs in a single file
- Select Export image in the File sub-menu.
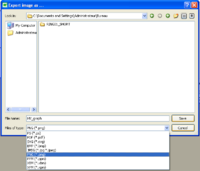
- Choose a destination folder, image format, and file name.
Another possibility is to save the graphic in a page format, compatible with Figue. In this case,