Difference between revisions of "Active source experiment (MASW)"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<br style="clear: both"/> | <br style="clear: both"/> | ||
| − | ===Description of the MASW toolbox === | + | === Description of the MASW toolbox === |
[[Image:MASW_ToolBox_Overview_new.png|thumb|right|400px|Overview of Masw toolbox]] | [[Image:MASW_ToolBox_Overview_new.png|thumb|right|400px|Overview of Masw toolbox]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* ''Curves'' tab is used to save, remove or load dispersion curves that are picked | * ''Curves'' tab is used to save, remove or load dispersion curves that are picked | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both"/> | ||
| + | === Parameters setting === | ||
| + | [[Image:MASW_Parameters_PREPROCESSING.png|thumb|right|300px]] | ||
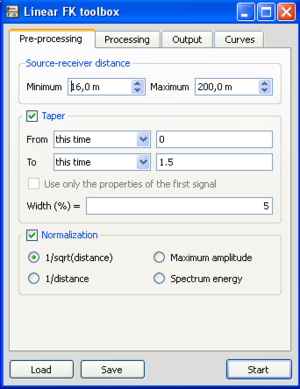
| + | In ''Pre-processing'' tab: | ||
| + | * Select the minimum and maximum source-to-receiver distance which will be processed. This allows to exclude signals close to the source shot (this distance should be at least one wavelength in order to reduce [[Geopsy:Active_source_experiment_(MASW)|near-field effects)]] or at large distances for which the signal-to-noise ratio may be low. | ||
| + | * Select the [[Geopsy:_Time_Limits|time limits]]to be processed. A taper | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 11 March 2010
Contents
General overview
First introduced by Al-Husseini et al. (1981), Mari (1984), Gabriels et al. (1987), the Multichannel analysis of surface waves was popularized by Park et al. (1999). This technique relies on the recording along a 1D linear profile of seismic signals produced by a controlled source (hammer, vibrator, explosion, etc.) and analysis of surface wave dispersion properties after applying slant-stack or FK transform to the recorded seismic section. In the following tutorial, only the FK transform is used.
Getting ready
- Download the compressed signal file.
- Launch Geopsy and set Rxxx as name in the Geopsy Loading Preferences.
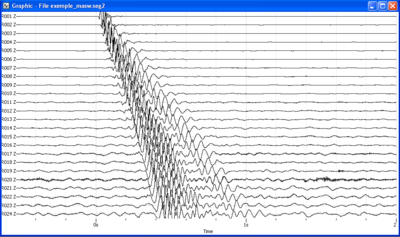
- Load and view these downloaded signals. A seismic section as the one displayed in the figure on the right should then appeared.
- Check in the Table signal viewer that sensors location is ranging from 0 to 92 meters with a 4 meters spacing.
- Check that source location is X=-4 meters by editing Set sources in Geopsy Edit menu. Alternatively, you can also add the Source X field in the Table signal viewer.
Description of the MASW toolbox
Open the MASW toolbox by pushing the following plugin icon ![]() or, alternatively, by selecting Linear F-K for active experiments in Tools menu.
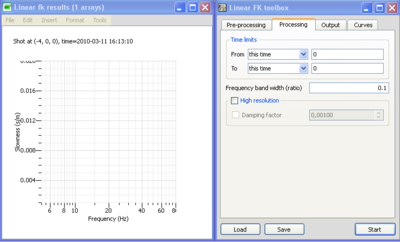
Two windows should then open as displayed in the figure on the right: the Linear FK toolbox to set up processing parameters and a Linear fk results to display MASW results. The Linear FK toolbox is composed of four tabs:
or, alternatively, by selecting Linear F-K for active experiments in Tools menu.
Two windows should then open as displayed in the figure on the right: the Linear FK toolbox to set up processing parameters and a Linear fk results to display MASW results. The Linear FK toolbox is composed of four tabs:
- Pre-processing tab is used to define the time window, the tapering, the amplitude normalization, etc.
- Processing tab allows to define the processing scheme (FK or HRFK)
- Output tab is used to set up the frequency and slowness band to be processed and the output filename
- Time tab allows to select the time limits and part of the signals to be processed and the time window length;
- Curves tab is used to save, remove or load dispersion curves that are picked
Parameters setting
In Pre-processing tab:
- Select the minimum and maximum source-to-receiver distance which will be processed. This allows to exclude signals close to the source shot (this distance should be at least one wavelength in order to reduce near-field effects) or at large distances for which the signal-to-noise ratio may be low.
- Select the time limitsto be processed. A taper
- HRFK (cross-link avec HRFK de Mathias)
- normalize energy
FK Computing
- computation for one single file and picking of the curve
- alternatives : 1) create a stack file and then compute the FK; 2)compute FK for all shots and then stack the FK maps