Difference between revisions of "H/V spectral ratio"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
This tool is used to obtain Horizontal to Vertical (H/V) spectral ratios from any type of vibration signals (ambient vibrations, earthquake…). The example used for explanations is an ambient vibration recording. | This tool is used to obtain Horizontal to Vertical (H/V) spectral ratios from any type of vibration signals (ambient vibrations, earthquake…). The example used for explanations is an ambient vibration recording. | ||
| − | The reference document for the H/V processing is the SESAME user guidelines, which is strongly recommended for further reading ("Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements, processing and interpretation" | + | The reference document for the H/V processing is the SESAME user guidelines, which is strongly recommended for further reading ("Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements, processing and interpretation" [http://SESAME-FP5.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr], 62 pages, April 2005). |
== Getting ready == | == Getting ready == | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 9 March 2010
This tool is used to obtain Horizontal to Vertical (H/V) spectral ratios from any type of vibration signals (ambient vibrations, earthquake…). The example used for explanations is an ambient vibration recording.
The reference document for the H/V processing is the SESAME user guidelines, which is strongly recommended for further reading ("Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements, processing and interpretation" [1], 62 pages, April 2005).
Contents
Getting ready
- Download compressed signal file.
- Load and view these downloaded signals.
- Select H/V in menu Tools (alternative ways to start a tool)
Window selection
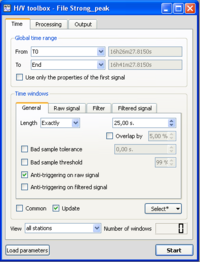
- Make sure you are in the Time tab, and that parameters are as in the example window.
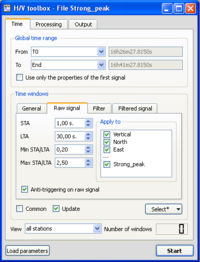
- Click on the Raw signal, to check that anti-trigger parameters are as in the example window.
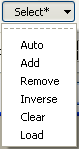
- Click on the Select button and select Auto.
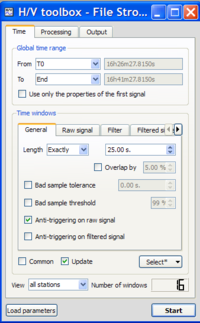
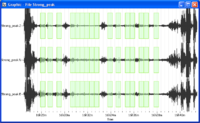
- The number of selected windows appears at the bottom right corner of the time tab.
The number of windows should be as in the example.
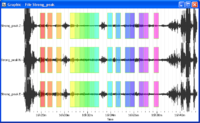
- Selected windows should appear as green rectangles on the signal viewer.
Processing parameters
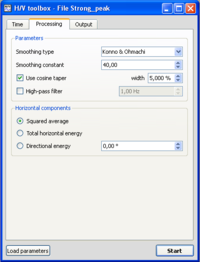
- Click on the Processing tab, and make sure that parameters are as in the example window.
Output parameters
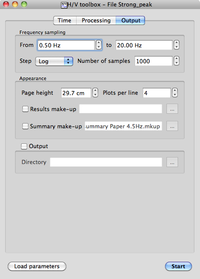
- Make sure you are in the Output tab, and that parameters are as in the example window.
Data processing
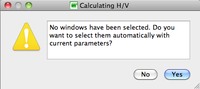
- In case no window selection has been performed, a pup-up window appears.
Simply click on the Yes button and processing will follow its way.
Results
Signal diplay
- Selected windows are colored, matching colours in he H/V graphics, i.e. colour of individual H/V curves have the same colour as the signal windows.
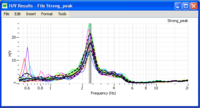
H/V curve
- The blak curve represents H/V averaged over all colored individual H/V curves The two dashed lines represent H/V standard deviation.
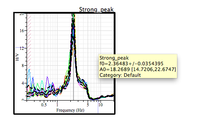
- The grey area represent the peak frequency and its standard deviation. The frequency value is at the limit between the dark and clear areas.
* Use the cursor to get values on the H/V curve. The exact value of the H/V peak frequency and its standard deviation may be obtained by sliding the cursor onto the H/V curve title (Strong_peak) in the upper right corner above the graphics.
Saving results
- The blak curve represents H/V averaged over all colored individual H/V curves The two dashed lines represent H/V standard deviation.
Changing H/V curve
Further readings
- Guillier et al. 1998,1999,2002,2003, 2004, 2005a, 2005b, 2005c, 2005d, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011
- Chatelain et al. 1985, 1987, 1998,1999,2002,2003a, 2004, 2008a, 2008b, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012a, 2012b
- Spectral ratios along a profile