Difference between revisions of "Dispersion curve inversion"
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=== Defining the parameter space === | === Defining the parameter space === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Defining the parameter is the key point of the inversion. At this step you have to figure out what information you already know about the ground structure and information you would like to extract. More details on [[Dinver Parameterization|parameterization strategies]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Activate the Parameterization panel in menu Tools. | ||
== Running the inversion == | == Running the inversion == | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 24 July 2009
This tutorial shows how to invert a dispersion curve measured for surface waves. It is based on dinverdc module used inside dinver framework.
Contents
Getting ready
Start Dinver with Surface Wave Inversion module.
At first glance, the interface might look a little bit messy. If it is the first time you start dinver, you'd better close all windows until having an empty workspace. The various tools will be displayed one by one and explained in this tutorial, in a logical order.
Importing the dispersion curve to fit
- Activate the Target panel in menu Tools.
- Select the Dispersion option. Leave the Misfit weigth and the Min. misfit to their default values, 1 and 0, respectively.
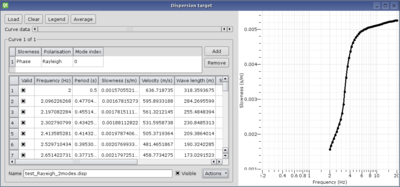
- Click on Set to load the dispersion curve, the Dispersion curve target is displayed.
Load a dispersion curve and fix its frequency sampling:
- Load this dispersion curve. It is a theoretical curve computed using this tutorial.
- Select the fundamental curve
- Use curve data scroll bar and visible button to identify it.
- This is the curve defined over the complete frequency range and with higher slowness).
- Re-sample it from 2 to 20 Hz on log scale with 50 samples (menu Actions/Resample).
- Cut it from 2 to 20 Hz (menu Actions/Cut).
- Select the first higher mode curve
- Use curve data scroll bar and visible button to identify it.
- This curve is not defined over the complete frequency range and it has a lower slowness).
- Remove it (menu Actions/Remove).
Achieving a good frequency sampling is an art, for a better understanding see Curve sampling.
At this step, the Dispersion curve target should contain only one curve, the fundamental mode. Make sure the mode table contains only one item like this:
Defining the parameter space
Defining the parameter is the key point of the inversion. At this step you have to figure out what information you already know about the ground structure and information you would like to extract. More details on parameterization strategies.
- Activate the Parameterization panel in menu Tools.