Difference between revisions of "Max2curve"
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
[[Image:Max2CurveGridStatistics.png|thumb|left|250px|Grid statistics window of max2curve]] | [[Image:Max2CurveGridStatistics.png|thumb|left|250px|Grid statistics window of max2curve]] | ||
| − | The '''Grid statistics window''' allows the user of max2curve to | + | The '''Grid statistics window''' allows the user of max2curve to have direct access to the |
| − | for each frequency. | + | individual histograms for each frequency. |
| − | the lowest to the highest frequency band. For | + | For scanning over different frequency bands, one can use the slider bar to scan from |
| − | the re-normalized histogram ( = pdf) of all slowness | + | the lowest to the highest frequency band. For each center frequency, one obtains |
| − | and sample standard deviation <math>\sigma(f_c)</math> calculated from the histogram are used | + | the re-normalized histogram ( = pdf) of all slowness/autocorr/ellipticity displayed in the upper panel. |
| − | to display the corresponding normal distribution <math>N(\mu(f_c),\sigma(f_c))</math>) as overlaying red curve. | + | The sample mean <math>\mu(f_c)</math> and sample standard deviation <math>\sigma(f_c)</math> calculated |
| + | from the histogram are used to display the corresponding normal distribution <math>N(\mu(f_c),\sigma(f_c))</math>) | ||
| + | as overlaying red curve. | ||
| − | The lower panel | + | The lower panel displays a different view of the same information. Here, a cumulative histogram or |
| − | [[Wikipedia:probability function|probability function]] instead of histogram and pdf. | + | [[Wikipedia:probability distribution function|probability distribution function]] instead |
| − | The display has been introduced because it is often easier to | + | of histogram and pdf. The display has been introduced because it is often easier to judge the |
| − | of | + | ''normalness'' of the distribution in the cumulative view. |
| − | Besides | + | Besides pure visualization, the grid statistics window can be further used to modify/edit/clean |
| − | the histograms on | + | the histograms. Please note that '''any editing must be done based on scientific reasoning'''. |
| − | the histogram picture. | + | E.g. if there is expert knowledge about the way aliasing phenomena are wrapped into the histogram picture in the |
| − | + | case of the f-k output files, then one has sufficient ground to eliminate parts of the observation from | |
| − | + | the histograms. | |
| + | |||
| + | The editing of histograms is performed by drawing a rectangular window on the region of the | ||
| + | histogram that is to be kept for interpretation. You enter the edit mode by right clicking on the upper panel | ||
| + | and enabling the ''selection'' button. | ||
<br style="clear: both"/> | <br style="clear: both"/> | ||
Revision as of 14:56, 12 March 2010
Visualization of analysis statistics
max2curve is a graphical user interface for visualization analysis results of various processing options in geopsy. max2curve reads, filters and determines histograms from .max files.
You may call max2curve on the command line directly with the output file (.max file) produced from your f-k processing.
$> max2curve your_output_file.max
Certainly you may also open max2curve directly. Then you will need to locate your .max file in the directory tree and select it with the automatically opened file browser.
max2curve then reads the contents of the .max output file and computes a probability density function (pdf) for slowness values (in case of f-k result files) or autocorrelation values (in case of MSPAC output files) for each individual frequency band of processing.
In order to be able to produce the pdf from re-normalization of a binned histogram, max2curve needs to know about:
- the slowness limits and the number of bins to use for the f-k output files.
- the ring and component index, limits for the autocorrelation values (-1,1 is a good choice) and number of bins to use for the spac output files.
- the limits of the ellipticity values (0.1,10 is a good choice) and number of bins to use for the H/V tfa output files.
An example for the usage of max2curve in either case are given in the FK tutorial, the MSPAC tutorial, and the H/V tfa tutorial, respectively.
Further, for each of the three output file types, it is possible to make a pre-selection or some filtering according to method specific criteria.
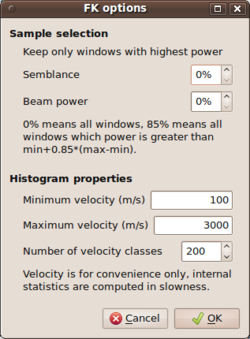
- For the f-k type output results, it is possible to filter the .max file(s) according to two extra criteria. Using the two entries under Sample selection, i.e. specify percentage values for Semblance and Beam power, it is possible to filter individual time window results falling below thresholds for the semblance coefficients and beam power values. Although semblance is a normalized quantity, we choose to develop a relative threshold scheme for filtering results for both semblance and beam power values. The percentage values should be understood as follows: for all entries in the .max output file, the minimum and maximum values for the semblance coefficient and the beam power values are used as lower (0%) and upper (100%) limits. Any given percentage value will compute the threshold as absolute value in between these two limits by linear interpolation. Note that the conditions are combined in the sense of a logical and. Only time window that surpass the threshold for both values (semblance and beam power) will be kept and passed to the histogram computation. Any other analysis window result will be skipped and is not taken into account for the computation of the frequency dependent histogram.
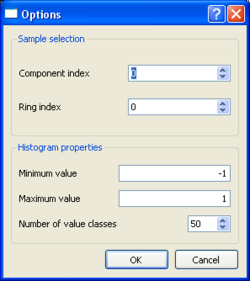
- For the MSPAC type output results, the results will be filtered according to some ring and component index. The output files contain the autocorrelation values for each ring and component for each analysed time window. For computing a histogram it makes only sense to select the results for one ring and component. Component indices from 0 to 2 (Vertical=0, Radial=1, Transverse=2) are only needed for 3C-MSPAC computation.
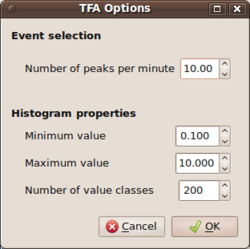
- For the HVTFA type output files, the criterion for selection is based on a maximum number of events per minute to be kept for the final analysis. NEEDS MORE DESCRIPTION (Mirjam??)
TO BE CONTINUED
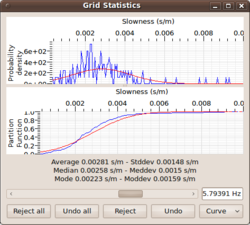
Grid statistics window
The Grid statistics window allows the user of max2curve to have direct access to the individual histograms for each frequency. For scanning over different frequency bands, one can use the slider bar to scan from the lowest to the highest frequency band. For each center frequency, one obtains the re-normalized histogram ( = pdf) of all slowness/autocorr/ellipticity displayed in the upper panel. The sample mean and sample standard deviation calculated from the histogram are used to display the corresponding normal distribution ) as overlaying red curve.
The lower panel displays a different view of the same information. Here, a cumulative histogram or probability distribution function instead of histogram and pdf. The display has been introduced because it is often easier to judge the normalness of the distribution in the cumulative view.
Besides pure visualization, the grid statistics window can be further used to modify/edit/clean the histograms. Please note that any editing must be done based on scientific reasoning. E.g. if there is expert knowledge about the way aliasing phenomena are wrapped into the histogram picture in the case of the f-k output files, then one has sufficient ground to eliminate parts of the observation from the histograms.
The editing of histograms is performed by drawing a rectangular window on the region of the histogram that is to be kept for interpretation. You enter the edit mode by right clicking on the upper panel and enabling the selection button.