Difference between revisions of "Geopsy: Map"
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A '''Map''' is a [[Geopsy: Signal Viewer|Signal viewer]] two-dimensional representation of | + | A '''Map''' is a [[Geopsy: Signal Viewer|Signal viewer]] two-dimensional representation of receivers coordinates in the XY plane for a set or a subset of signals. It can be created using the [[Geopsy: View menu|View menu]] and then [[Geopsy: Signal drag&drop|drag and drop]] the set of signals of interest in the graphic viewer. [[Geopsy: Signal drag&drop|Drag and drop]] signals directly on the graphic icon in the [[Geopsy: Toolbar|toolbar]] produces the same. |
| − | The geographical coordinates of the receivers are set using the [[Geopsy: Edit | + | The geographical coordinates of the receivers are set using the [[Geopsy: Edit menu#Set receiver|Edit menu]] |
The various actions that can be performed with a subset of signals in a map are described in [[Geopsy: Signal Viewer|Signal viewer]] entry. | The various actions that can be performed with a subset of signals in a map are described in [[Geopsy: Signal Viewer|Signal viewer]] entry. | ||
| − | + | A map makes use of the general [[SciFigs: Graph|Graph object]] from the [[SciFigs| Scifigs library]]. The area of a map is partitioned in the same way as a [[Geopsy: Graphic|graphic viewer]]. The main layer is a XYNamePlot which means that signals (or stations) are represented by configurable symbols (shape, size, color, ...) and by their names the relative positions of which can be adjusted (top, left, right, bottom, distance). To create plots suitable for publication, you can save the XY plot to a [[Xml files|page file]] and customize the presentation into [[SciFigs: Figue|figue]]. | |
==Map scale== | ==Map scale== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:map_select.png|thumb|right|400px|Selection of signals on a map viewer. Two stations are selected.]] | |
| − | + | Scales of maps are intrinsic properties of [[SciFigs: Graph| Graph objects]]. Some tips are given here. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Both X and Y axis have by default the same scale. The scale is automatically adjusted so that all the receiver coordinates of the signals contained in the [[Geopsy: Signal Viewer|viewer]] remain visible. Resizing the viewer has no effect on the scale, it changes only the axis minimum and maximum values. To change the scale, edit the axis [[SciFigs: Graph#Properties|properties]] under category ''Scale''. Modify the size ''Scaled'' (e.g. 1/400, for 1cm=4m). Make sure the scales are the same for X and Y axis to avoid distortions. Alternatively, you can resize the map viewer (this saves the size to the user settings). Then create a new viewer with the drag and drop mechanism (or redo the what you did to create the present one): | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * Enter the selection mode (see hereafter) | |
| + | * Select all signals | ||
| + | * Leave the selection mode | ||
| + | * Drag and drop the Map content to Map item in toolbar to create a new Map. | ||
| − | + | ==Signal selection== | |
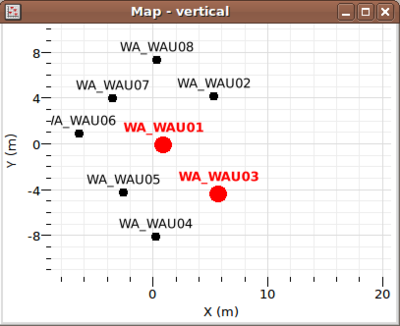
| − | The drag and drop mechanism is deactivated when the "Zooming" or the " | + | Apart from the visualization, maps offer the advantage over tables that you can select station according to their localizations. In the active map, right-click on the mouse to activate the context menu, select "Select stations". The object switch to the selection mode ("Select stations" is checked). When you press and move the mouse in this mode, a dotted rectangle is displayed. When releasing the mouse, all coordinates that fall within this rectangle are selected (marked as bold and red), others are deselected. To select more signals, press SHIFT at the same time. To leave the the "Select stations" mode hit CTRL+SHIFT+e (CMD+SHIFT+e for Mac) or deselect "Select stations" by right-click again. If several signals have the same coordinates they are indistinctly selected together. |
| + | |||
| + | The [[Geopsy: Signal drag&drop|drag and drop mechanism]] is deactivated when the "Zooming" or the "Select stations" mode is switched on. To move the selected signals to another viewer, first leave these modes. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:10, 11 March 2010
A Map is a Signal viewer two-dimensional representation of receivers coordinates in the XY plane for a set or a subset of signals. It can be created using the View menu and then drag and drop the set of signals of interest in the graphic viewer. Drag and drop signals directly on the graphic icon in the toolbar produces the same.
The geographical coordinates of the receivers are set using the Edit menu
The various actions that can be performed with a subset of signals in a map are described in Signal viewer entry.
A map makes use of the general Graph object from the Scifigs library. The area of a map is partitioned in the same way as a graphic viewer. The main layer is a XYNamePlot which means that signals (or stations) are represented by configurable symbols (shape, size, color, ...) and by their names the relative positions of which can be adjusted (top, left, right, bottom, distance). To create plots suitable for publication, you can save the XY plot to a page file and customize the presentation into figue.
Map scale
Scales of maps are intrinsic properties of Graph objects. Some tips are given here.
Both X and Y axis have by default the same scale. The scale is automatically adjusted so that all the receiver coordinates of the signals contained in the viewer remain visible. Resizing the viewer has no effect on the scale, it changes only the axis minimum and maximum values. To change the scale, edit the axis properties under category Scale. Modify the size Scaled (e.g. 1/400, for 1cm=4m). Make sure the scales are the same for X and Y axis to avoid distortions. Alternatively, you can resize the map viewer (this saves the size to the user settings). Then create a new viewer with the drag and drop mechanism (or redo the what you did to create the present one):
- Enter the selection mode (see hereafter)
- Select all signals
- Leave the selection mode
- Drag and drop the Map content to Map item in toolbar to create a new Map.
Signal selection
Apart from the visualization, maps offer the advantage over tables that you can select station according to their localizations. In the active map, right-click on the mouse to activate the context menu, select "Select stations". The object switch to the selection mode ("Select stations" is checked). When you press and move the mouse in this mode, a dotted rectangle is displayed. When releasing the mouse, all coordinates that fall within this rectangle are selected (marked as bold and red), others are deselected. To select more signals, press SHIFT at the same time. To leave the the "Select stations" mode hit CTRL+SHIFT+e (CMD+SHIFT+e for Mac) or deselect "Select stations" by right-click again. If several signals have the same coordinates they are indistinctly selected together.
The drag and drop mechanism is deactivated when the "Zooming" or the "Select stations" mode is switched on. To move the selected signals to another viewer, first leave these modes.