Ambient vibration array
Contents
Common pre-requisites for array processing - getting ready
Loading signals
View time series
Group signals
Insert / edit station coordinates
F-K Toolbox (conventional f-k)
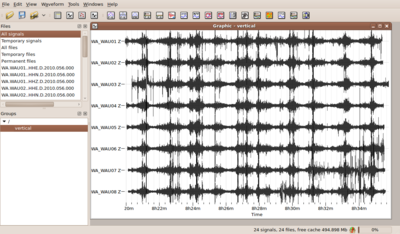
If you have followed all steps above you should have now a set of simultaneously recorded waveforms building a group and containing coordinates for each waveform. You can view this group of waveforms in the data viewer and should get a picture like the one shown to the right.
Now you can open the conventional frequency wavenumber toolbox by pushing the plugin icon ![]() .
.
The f-k toolbox should open and is now attached to the signal viewer. No other toolbox will now open with the signals you have loaded to the signal viewer. In order to process the same data set by another tool, you have to open them in a different signal viewer window. Note also, that once you close either the f-k toolbox window or the signal viewer, there is no way to undo this action - you will have to start again by opening a new signal viewer and attaching the f-k toolbox to it. Alternatively you can drag your group directly into the f-k toolbox icon. Geopsy will automatically open a new exclusively attached signal viewer for you.
Let's now have a close look to the individual parameters to be set in the f-k toolbox. There are four main groups of parameters to be considered.
- Pre-processing parameters for excluding data from processing.
- Processing parameters for selecting time windows on the remaining data.
- Processing parameters for selecting narrow frequency bands for processing
- Parameters related to the output of results from f-k processing.
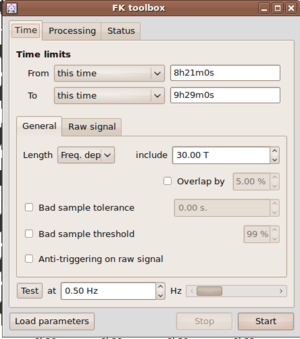
These parameters are laid out in different parts of the f-k toolbox widget. Note, that the toolbox has three main tabs: Time, Processing and Status.
The pre-processing parameters for excluding data from processing follow the same argumentation as the data selection for other toolboxes like H/V processing and can be found in the Time tab.
E.g. one can apply the so-called anti-trigger approach for removing transient signals from the continuous recordings (i.e. excluding those time chunks from processing). The anti-trigger approach can be applied to raw or filtered data. For the detailed settings please look into the description of anti-trigger. Another, second, approach for excluding data from processing is provided via the bad sample approach. For details in setting parameters with the bad sample approach check this page.
There are two distinct inputs in the f-k toolbox for selecting time windows for processing.
First, it is necessary to specify start and end times of the overall data window for processing
by selecting entries From and To in the Time limits part of the Time tab of the fk-toolbox
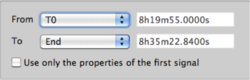 .
.
There are three options each for the
drop boxex From and To. For the From entry you can select among 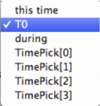 .
.
- this time (entries in form xx h xx m xx.xxx s)
- T0 (selects earliest common start time of all traces in group)
- during (selects time duration before end of the signals - either specified with End or this time as explained below)
For the To entry there are the options 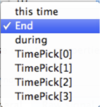 :
:
- this time (entries in form xx h xx m xx.xxx s)
- End (selects latest common end time of all traces in group)
- during (selects time duration from start time as given above - either specified by this time or T0)
Note: a selection of time limits as From: during && To: during is NOT valid.
Processing parameters for selecting the time windows on the remaining data
Saving results / contents of output file
Graphical display of f-k results using max2curve
High resolution frequency wavenumber Toolbox (Capon's method)
Saving results / contents of output file
Graphical display of f-k results using max2curve
Modified Spatial Autocorrelation (MSPAC) Toolbox
The Modified Spatial Autocorrelation (MSPAC) was introduced by Bettig et al. (2001) [1] after pioneer paper of Aki (1957). [2] This method allows computing spatial autocorrelation coefficients for any arbitary array layouts.
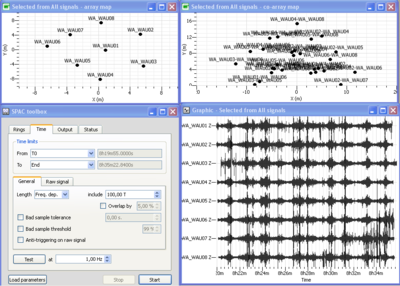
After viewing the group of waveforms in the data viewer, open the MSPAC toolbox by pushing the following plugin icon ![]() . Alternatively you can drag your group directly into the SPAC toolbox icon. The SPAC toolbox should now be attached to the signal viewer.
. Alternatively you can drag your group directly into the SPAC toolbox icon. The SPAC toolbox should now be attached to the signal viewer.
Four windows should then opened as displayed in the figure on the right: (1) a signal time viewer, (2) a map displaying array station locations, (3) a map displaying co-array stations location and (4) the SPAC processing toolbox. This processing toolbox is composed of four sub-menus: "Rings" sub-menu is used to design rings from the co-array; "Time" is used to define begin and end time to be processed, time window length, anti-triggering options as described in section XXX; "Output" menu is used to set up the output frequency band together with the sampling scale type (linear, log) and number of frequencies, the output filename; "Status" menu provides information about computing status. All these sub-menus are described hereafter.
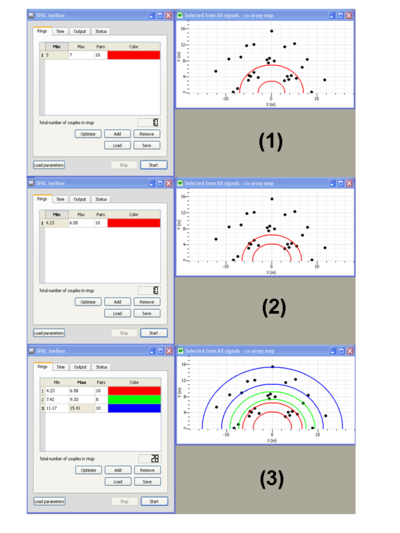
Defining rings
Saving results / contents of output file
Graphical display of f-k results using spac2disp
spac2disp
References
- ↑ Bettig B., P.-Y. Bard, F. Scherbaum, J. Riepl, F. Cotton, C. Cornou, D. Hatzfeld, 2001. Analysis of dense array measurements using the modified spatial auto-correlation method (SPAC). Application to Grenoble area., Boletin de Geofisica Teoria e Applicata, 42, 3-4, 281-304.
- ↑ Aki, K., 1957. Space and Time Spectra of Stationary Stochastic Waves, with Special Reference to Microtremors, Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Tokyo, 35, 415-457.