Difference between revisions of "Geopsy: Set header"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
All formulas are separated by ''';''' (like in C). If a line begins with '''//''', all text is ignored until the end of the line (like C comments). The same way, all text included between '''/*''' and '''*/''' is considered as a comment. Commenting parts of an equation may be interesting to solve errors. | All formulas are separated by ''';''' (like in C). If a line begins with '''//''', all text is ignored until the end of the line (like C comments). The same way, all text included between '''/*''' and '''*/''' is considered as a comment. Commenting parts of an equation may be interesting to solve errors. | ||
| − | The general syntax is : | + | The general syntax is : |
| + | SignalData = value. | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both"/> | ||
There are various assignment operators: | There are various assignment operators: | ||
| − | + | * SignalData = value : Set SignalData to value. This operator works for numbers and character strings | |
Revision as of 10:21, 11 March 2010
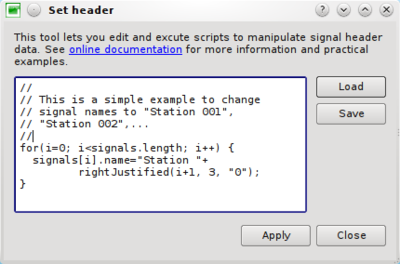
This section explains how to modify header information stored in a database in a very efficient way. Any information about signals can be viewed in a table. Signals can be modified one by one by cell editing (Ctrl+K). For huge number of signals this is boring and time consuming. Instead, you can create formulas and apply them with one single click. The syntax for these formulas is rather simple.
General presentation
From any active signal viewer (which is by definition a list of signals), click on menu item Edit/Set headers. A dialog box will appear. You can type any number of equations in the left editor. To assist you, for instance for a correct spelling of signal field names, you can use the combos Variables, usual operators and Functions 
All formulas are separated by ; (like in C). If a line begins with //, all text is ignored until the end of the line (like C comments). The same way, all text included between /* and */ is considered as a comment. Commenting parts of an equation may be interesting to solve errors.
The general syntax is :
SignalData = value.
There are various assignment operators:
- SignalData = value : Set SignalData to value. This operator works for numbers and character strings
You may also save the current equations in a file (*.headqu) and load it later.