Difference between revisions of "Warangps"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== <math>k_{min}</math> == | == <math>k_{min}</math> == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:WarangpsFKResponse.png|thumb|right|450px|Array response function in wavenumber domain]] | ||
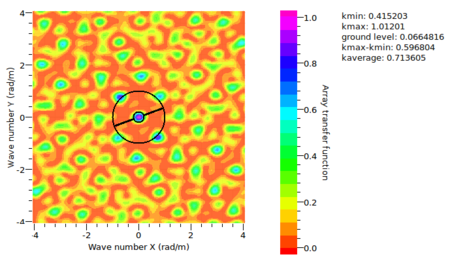
| + | <math>k_{min}</math> is used to quantify the resolution capabilities of a specific array geometry. The definitionis based on the following idea: | ||
| + | Given two signals propagating with similar wavenumbers, what is the minimum distance between wavenumbers that will still allow to find two | ||
| + | separated peaks in the wavenumber map? You will find several answers to this question depending on the signal properties (correlated, non-correlated) | ||
== <math>k_{max}</math> == | == <math>k_{max}</math> == | ||
== Typical usage == | == Typical usage == | ||
Revision as of 08:48, 11 March 2010
Warangps - Overview
Warangps is a graphical tool for displaying the status and coordinates of gps devices in a distributed sensor network. Among other things (to be described later), warangps can be used to display the array response function for a specific array geometry.
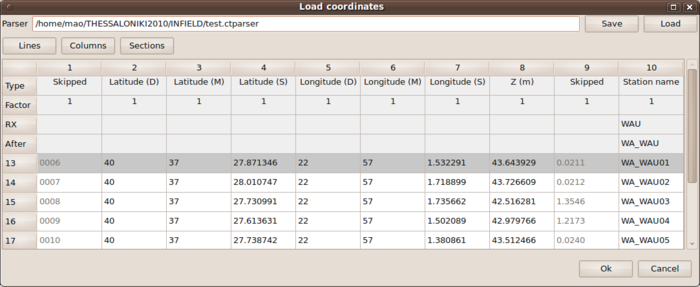
Loading coordinates
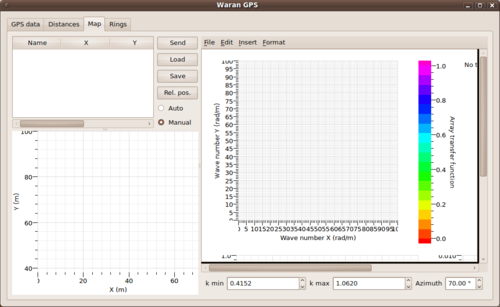
After starting up warangps, you should switch to the Map tab of the graphical user interface and set the radio button from Auto to Manual. Only then you are able to push the Load button to open a free format ASCII coordinate file.
After locating an appropriate file with the file browser, a file parser window will be opened. The flexibel parser is described in detail in the multi-column parser page. Here we provide an example coordinate file and a corresponding parser file.
After loading the pre-configured parser file or after specifying the different column entries by yourself for your own coordinate file, you will load the coordinates by confirming with the Ok button.
The displays in warangps will change immediately presenting the coordinates in a table (upper left) and on a map (lower left). The array response function (ARF) for the corresponding array geometry will be computed in the wavenumber domain and is displayed in the right drawing area of warangps. On top of the wavenumber map, two circles are drawn for automatically determined values of and . Details about the meaning of those quantities and the automatic computation from the array geometry are given below in the corresponding sections.
Besides the ARF, there are two more useful visualizations derived from the array response function:
- Directly below the ARF figure, 1-D cross sections along different look directions for the wave propagation are plotted. The grey lines in the background show cross sections in all directions in 2 degree steps. The black curve displays a cross section along the direction chosen in the Azimuth spin box located on the right below the drawing area. The black curve is only drawn in between the two circles for and .
- On the lower right of the drawing area, you will find a display of 4 distinct wavenumber values, , , , , as curves in frequency vs. slowness which finally provide information on the capabilities of the array geometry in terms of resolution and expected aliasing features (see below and ). The intention of this plot is to export the layer of this curve that can then be overlaid to the display of f-k analysis results in max2curve.
is used to quantify the resolution capabilities of a specific array geometry. The definitionis based on the following idea: Given two signals propagating with similar wavenumbers, what is the minimum distance between wavenumbers that will still allow to find two separated peaks in the wavenumber map? You will find several answers to this question depending on the signal properties (correlated, non-correlated)